Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Synthetic fibrous hydrogels as a platform to decipher cell–matrix mechanical interactions

Spreading of cells correlates with hydrogel stiffness. (A) Phase

Nanoscale Surface Topography Reduces Focal Adhesions and Cell Stiffness by Enhancing Integrin Endocytosis
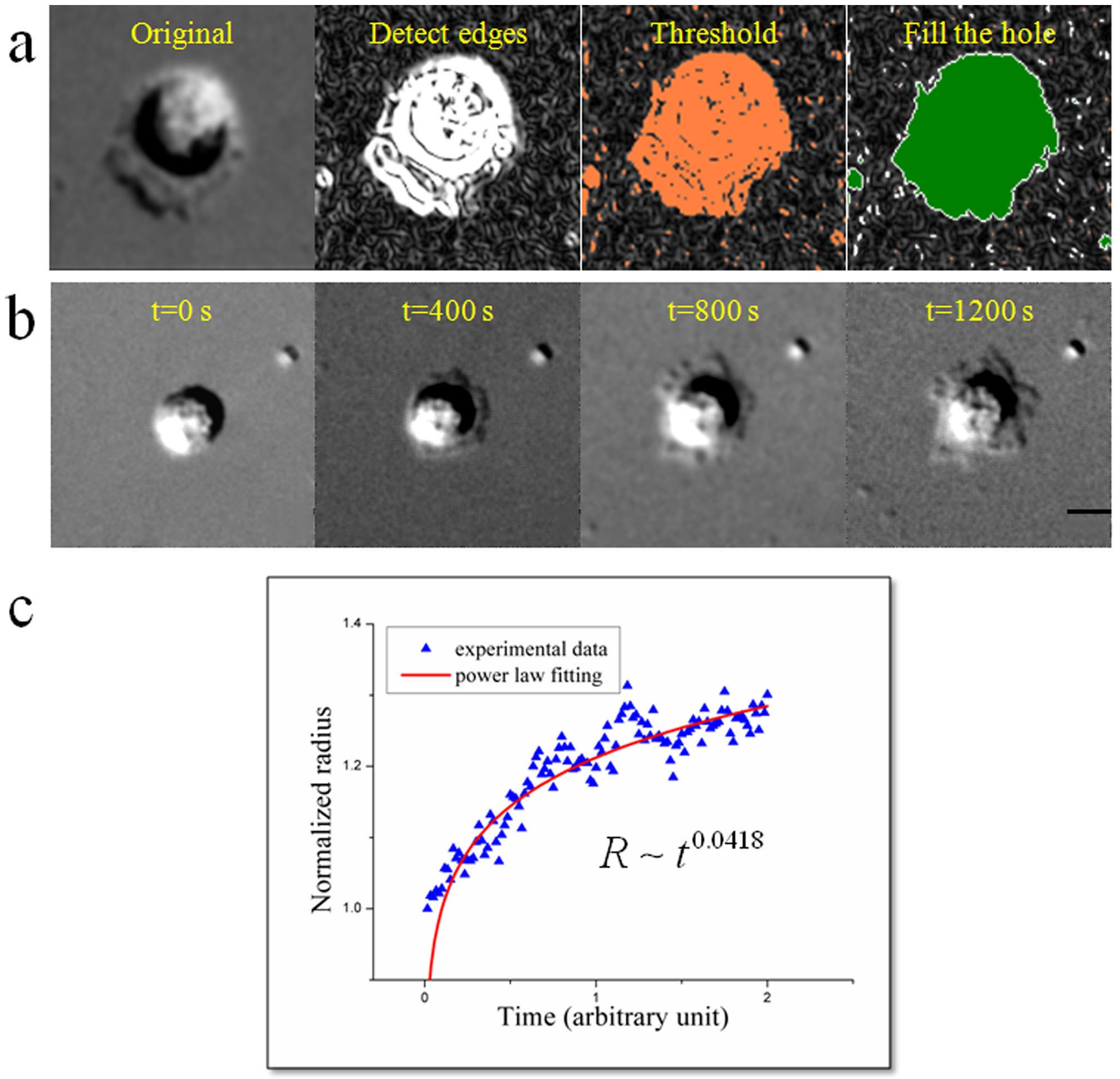
Kinetic behaviour of the cells touching substrate: the interfacial stiffness guides cell spreading
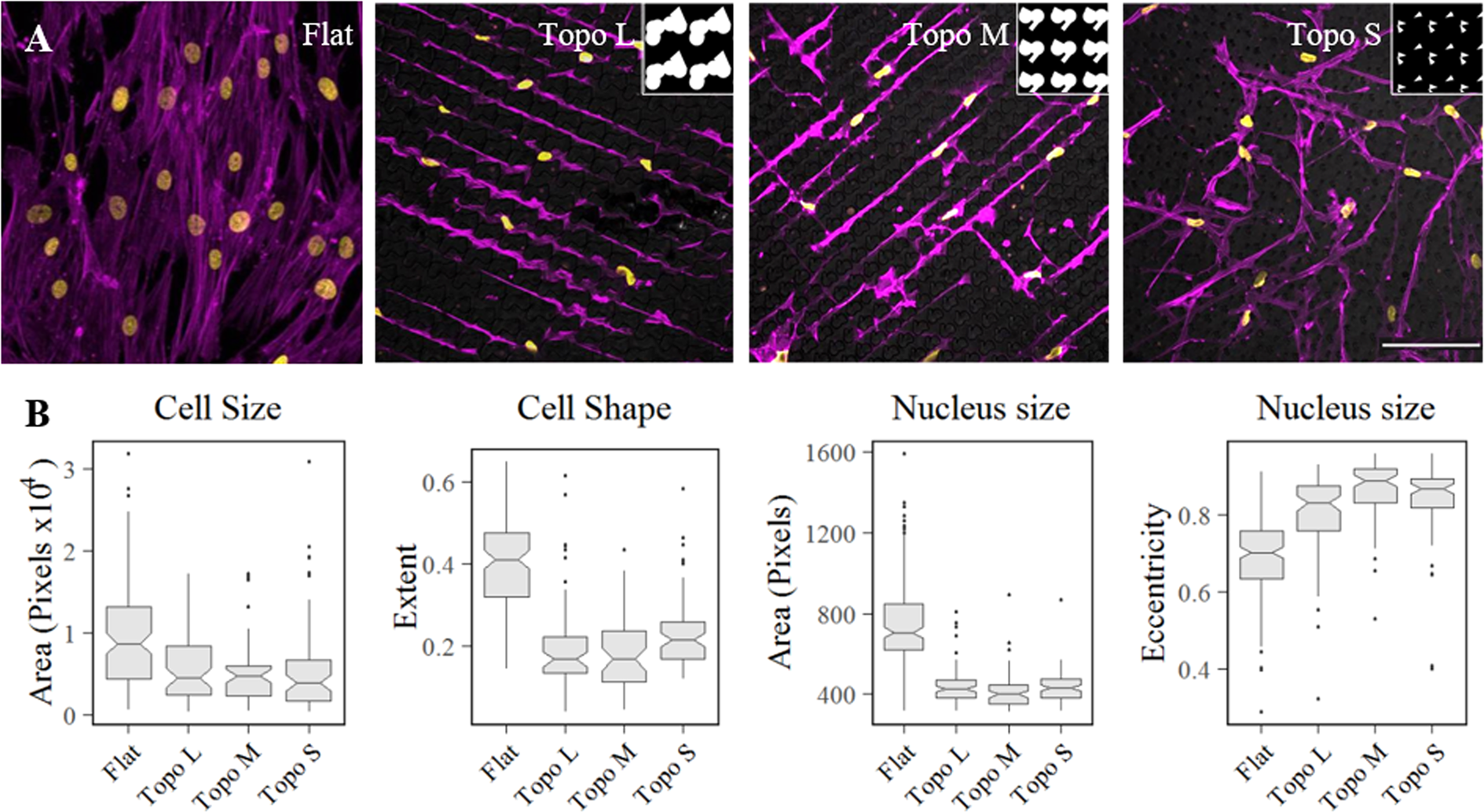
Dynamic adaptation of mesenchymal stem cell physiology upon exposure to surface micropatterns

Overview of vascular induction to examine the role of stiffness from
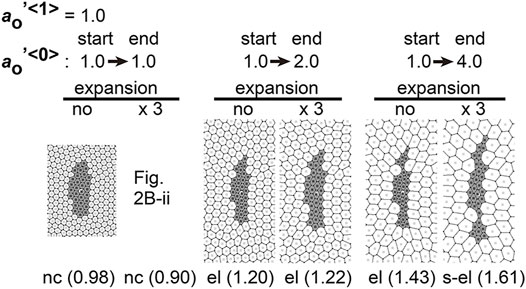
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface
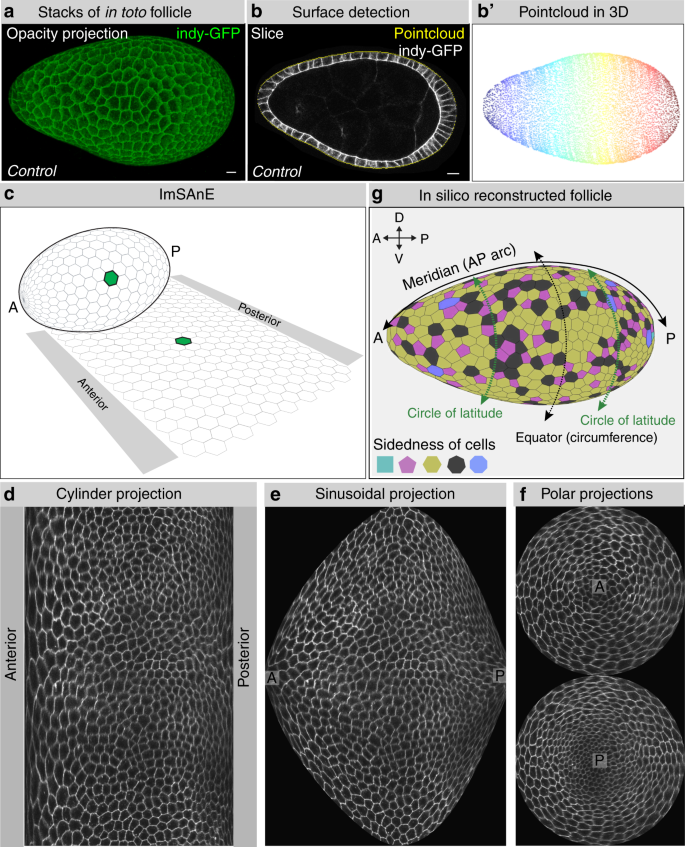
Extracellular matrix stiffness cues junctional remodeling for 3D tissue elongation

Biomechanics of cells and subcellular components: A comprehensive review of computational models and applications - Wang - 2021 - International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering - Wiley Online Library

Bioactivation of 3D Cell-Imprinted Polydimethylsiloxane Surfaces by Bone Protein Nanocoating for Bone Tissue Engineering
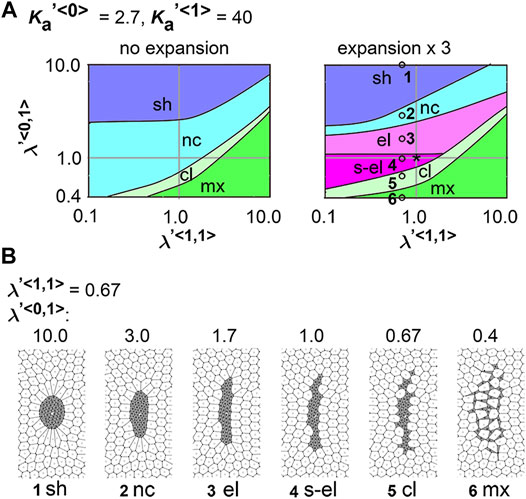
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface

How Hydrogel Stiffness Affects Adipogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells under Controlled Morphology
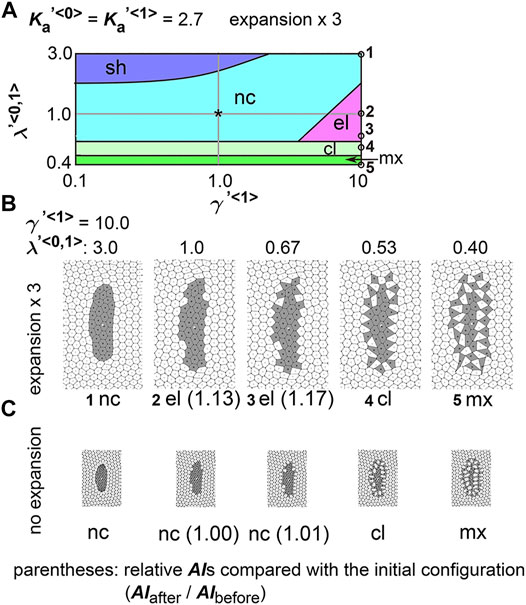
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)