PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
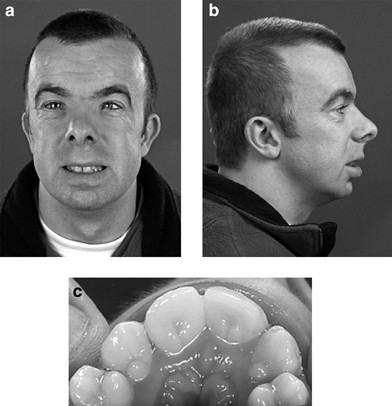
A typical six-month-old girl with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome was presented with typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate. Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome (RTS) was first described by Michail et al[1] and subsequently by Rubinstein and Taybi[2]. We present a typical six-month-old girl with RTS. Her mother had ovarian cancer and polyhydramnios during the pregnancy. Parents are closely related. There were frequent respiratory infections resulting in two hospital admissions. Physical examination revealed typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate (Fig. 1). A history of increased tearing was compatible with nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Other features include general hypotonia with delayed developmental milestones, short and broad thumbs and toes (Fig. 1). Chest x-ray showed cardiomegaly (Fig. 2). She had normal karyotype.
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/76d00455660f8d0dfa42fcd70278635b6c0e6ff5/2-Figure2-1.png)
PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41372-019-0506-7/MediaObjects/41372_2019_506_Fig5_HTML.png)
Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: is early transcatheter closure a paradigm shift?
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/full/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41598-019-52936-6/MediaObjects/41598_2019_52936_Fig1_HTML.png)
Characteristics of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Congenital Rubella Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/23239728_Rubinstein-Taybi_syndrome_with_normal_FISH_result_and_CREBBP_gene_analysis_A_case_report/links/543b70560cf24a6ddb9770bd/largepreview.png)
PDF) Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome with normal FISH result and CREBBP gene analysis: A case report
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1058981319301821-gr1.jpg)
Transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus in a tiniest baby – 510 grams - ScienceDirect
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pda27-230801062905-99c999e9/85/pda-27723pptx-2-320.jpg?cb=1690871679)
pda 27.7.23.pptx
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S193687981631545X-gr1.jpg)
Transcatheter Closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Extremely Premature Newborns: Early Results and Midterm Follow-Up - ScienceDirect
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/e26024cbcda91686a23ad5772202713ea6665ad7/2-Figure2-1.png)
PDF] Patent ductus arteriosus closure using an Amplatzer ventricular septal defect closure device in adulthood
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/e26024cbcda91686a23ad5772202713ea6665ad7/3-Figure4-1.png)
PDF] Patent ductus arteriosus closure using an Amplatzer ventricular septal defect closure device in adulthood
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/615919/fped-08-615919-HTML/image_m/fped-08-615919-g002.jpg)
Frontiers Transcatheter Closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Premature Infants With Very Low Birth Weight
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.mdpi.com/jpm/jpm-13-01263/article_deploy/html/images/jpm-13-01263-g001.png)
JPM, Free Full-Text
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/lw685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1186%2F1750-1172-4-17/MediaObjects/13023_2008_Article_151_Fig3_HTML.jpg)
Patent arterial duct, Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://rc.rcjournal.com/content/respcare/67/5/594/F1.large.jpg)
Definitive Closure of the Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Infants and Subsequent Short-Term Respiratory Outcomes
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)